Seasonal Vegetable Gardening: What to Plant and When

Seasonal vegetable gardening is an advantageous way to grow your food while fostering a deeper connection with nature. This practice involves understanding the optimal times to plant various vegetables based on the changing seasons, which can greatly influence their growth and flavor.
By familiarizing yourself with your local climate and the specific needs of different vegetables, you can choose the right crops for your garden, ensuring they are well-suited to the conditions they will face.
This knowledge helps you select the appropriate vegetables, maximizes your yield, and enhances the overall vegetable gardening experience. Planting at the correct time is crucial, as it ensures that your plants thrive in their ideal conditions—leading to healthier growth, vibrant colors, and a more fruitful harvest.
Moreover, seasonal vegetable gardening allows you to enjoy a diverse array of fresh produce throughout the year, from crisp spring greens to hearty winter root vegetables.
By following the seasonal calendar and actively engaging with your vegetable gardening, you can savor the satisfaction of harvesting your homegrown fruits and vegetables, benefiting our health and palate.
Table of Contents
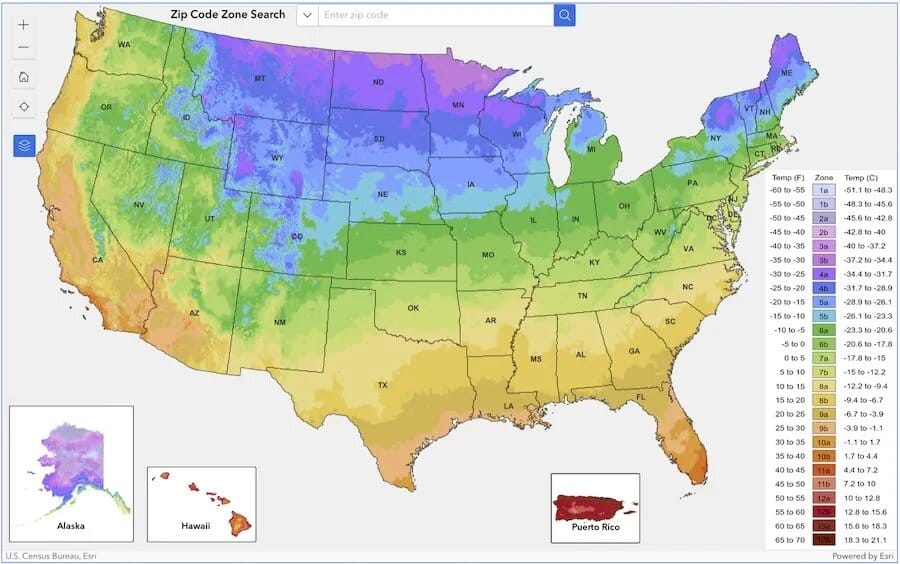
1. Understanding Your Growing Zone
Understanding your growing zone is essential for successful vegetable gardening. Growing zones, also known as hardiness zones, are geographic areas that reflect the climate and the average minimum temperatures of a region.
This classification helps gardeners identify which plants are most likely to thrive in their local conditions. Each zone is typically divided into two parts, indicated by a number and a letter (e.g., 5a, 5b), allowing for more precise guidelines on which vegetables to plant.
To determine your growing zone, you can use the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, easily accessible online. Simply find your location on the map, and you’ll see the corresponding zone. Additionally, local gardening centers or extension services can provide detailed information about your specific area.
By knowing your growing zone, you can make informed decisions on the best vegetables to grow, ensuring that they flourish and yield an abundant harvest in your vegetable gardening.
2. Cool-Season Vegetables
Cool-season vegetables thrive in the cooler weather of early spring and fall. These vegetables are more tolerant of frost and can grow well when temperatures are mild.
Here’s a list of popular cool-season vegetables:

Spinach: Plant in early spring or late summer for a fall vegetable gardening harvest. Harvest young leaves for tender greens in about 6-8 weeks.
Broccoli: Best planted in early spring or late summer. You can harvest the main head in 70-100 days, with side shoots continuing to produce after the main harvest.


Carrots: Sow seeds in early spring or late summer. Harvest in about 70-80 days for sweet and crunchy roots, or leave them until after the first frost for enhanced flavor.
Lettuce: Plant in early spring or fall. Leaf varieties can be harvested in as little as 30 days, while head types take about 60 days.


Peas: Sow seeds in early spring, as soon as the soil can be worked. Harvest in 60-70 days for sweet, fresh peas.
By correctly timing your planting and harvest, you can enjoy these nutritious vegetables at their peak freshness while making the most of the cooler seasons in your vegetable gardening.
3. Warm-Season Vegetables
Warm-season vegetables thrive in summer heat and require warmer soil temperatures to grow effectively.
Here are some popular warm-season vegetables to consider for your garden:

Tomatoes: Best planted after the last frost, typically in late spring. Depending on the variety, they can be harvested in 60-100 days.
Peppers: Plant peppers in late spring once the soil is warm. Harvest times vary, but most peppers can be picked within 70-90 days of planting.


Cucumbers: Sow seeds in late spring when temperatures are consistently warm. They usually take about 50-70 days to reach maturity.
Zucchini: Plant in late spring when the soil is warm, and you can expect to harvest in about 50-70 days.


Squash: Summer squash can be planted in late spring, typically yielding fruit in 50-65 days.
To ensure a successful harvest, aim to plant warm-season vegetables after your area’s last frost date and monitor the growing conditions closely to maintain healthy plants in your vegetable gardening.
Harvest them when they are ripe for peak flavor and nutrition.
4. Extending the Growing Season
Extending the growing season allows you to maximize your garden’s productivity and enjoy fresh vegetables for longer.
Here are some effective techniques to help you achieve this:

Row Covers: Lightweight fabric row covers can protect your plants from frost and pests while allowing sunlight and moisture to penetrate. Use them to cover your cool-season crops in the early spring or late fall to keep the soil warm and promote growth.
Cold Frames: A cold frame is a simple structure, usually made of transparent materials, that captures heat from the sun to create a warmer microclimate for your plants. Placing a cold frame over your vegetable gardening beds allows you to start seeds earlier in the spring and continue growing through the fall and winter months.


Succession Planting: By planning several rounds of planting for particular crops, you can harvest consistently throughout the season. After harvesting early crops like lettuce or spinach, sow a second crop, such as radishes or beets, in the same space to make the most of your garden plot.
Container Gardening: Using pots or containers to grow vegetables can be advantageous for extending your growing season. You can move containers indoors or into a sheltered space when temperatures drop, extending the life of your plants.

By implementing these techniques, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest beyond the traditional growing periods, making your vegetable gardening efforts even more rewarding.
5. Planning Your Garden Layout
Planning your garden layout is crucial for maximizing space, ensuring healthy plant growth, and promoting efficiency in your gardening efforts. A well-organized garden helps prevent overcrowding, allowing each plant to receive adequate sunlight, air, and nutrients.
By considering factors such as plant height, spread, and nutrient needs, you can create a layout that supports both growth and ease of maintenance.
Importance of Garden Layout and Companion Planting
Companion planting is a technique that involves placing certain plants near each other to enhance growth and deter pests. For example, planting marigolds alongside vegetables can help repel harmful insects, while combining legumes with heavy feeders, like corn, can improve soil fertility.
Planning your garden with companion planting in mind not only promotes a healthy ecosystem but also optimizes space, making your vegetable gardening more productive.
Sample Layouts for Optimal Growth

- The Block Layout: Organise your garden into blocks or sections for each type of vegetable. For example, dedicate one block to tomatoes, peppers, and basil, which all thrive together. This approach is visually appealing and makes watering and maintenance easier.
2. The Row Layout: Plant in straight rows, with taller plants at the back and shorter ones in the front. This simple design allows for easy access and good light exposure. A classic example is a row of corn at the back, followed by beans, lettuce, or radishes.


3. The Square Foot Garden: Divide your garden into square foot sections, planting different vegetables in each square based on their spacing needs. This method maximizes yield from a small area and simplifies planting and maintenance.
4. The Companion Circle: Create circles within your garden plot, grouping companion plants. For instance, a circle of lettuce can be surrounded by carrots and radishes, which grow well together and utilize the space efficiently.

By thoughtfully planning your garden layout and incorporating companion planting strategies, you can create a thriving vegetable gardening space that provides an abundance of fresh produce throughout the growing season.
6. Soil Preparation
Healthy soil is the foundation of successful vegetable gardening. It provides essential nutrients, supports root development, and retains moisture, all contributing to strong plant growth. Prioritizing soil health ensures that your vegetables thrive and yields are maximized in your vegetable gardening.
Importance of Healthy Soil for Vegetable Growth
Good soil quality influences not only plant growth but also pest resistance and the overall health of your garden ecosystem. Nutrient-rich soil helps plants absorb water and essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Healthy soil also promotes beneficial microorganisms that enhance nutrient availability and improve soil structure, leading to better drainage and aeration.
How to Assess and Improve Soil Quality
To start, assess your soil’s quality by performing a soil test, which measures pH levels and nutrient content. Most vegetables prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH (around 6.0 to 7.0). If tests reveal a low pH, you can adjust it by adding lime; conversely, adding sulfur can lower high pH levels.
Improving soil quality often involves incorporating organic matter, such as compost, well-rotted manure, or peat moss. These materials enhance soil structure, increase nutrient content, and promote beneficial microbial activity.
Additionally, practicing crop rotation and cover cropping can help maintain soil health by preventing nutrient depletion and reducing pest build-up.
By taking these steps to prepare and improve your soil, you can create an environment that supports thriving vegetable plants and leads to a bountiful harvest in your vegetable gardening.
7. Watering and Fertilizing
Proper watering and fertilizing are key components of successful vegetable gardening. Adequate moisture and nutrients greatly influence plant health, growth rates, and overall yields.
Understanding best practices for watering and the different types of fertilizers available will help you cultivate a flourishing vegetable gardening space.
Best Practices for Watering Vegetables
- Consistent Schedule: Aim to water your vegetables consistently, preferably early in the morning or late in the afternoon. This timing allows water to soak into the soil without excessive evaporation.
- Deep Watering: Water deeply and less frequently to encourage deep root growth. Applying 1-2 inches of water per week is typically sufficient, but this may vary depending on the weather and soil type.
- Soil Moisture Monitoring: Check soil moisture regularly by feeling the soil a couple of inches below the surface. If it’s dry, it’s time to water. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot and other issues.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of mulch around your plants helps retain soil moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds, reducing the need for frequent watering.
Types of Fertilizers
Fertilizers come in various forms, with organic and synthetic options being the most common.
- Organic Fertilizers: Derived from natural sources, such as compost, manure, or bone meal, organic fertilizers improve soil health over time by adding beneficial microbes and nutrients. They typically release nutrients more slowly, providing a steady supply for plants. Use organic fertilizers when planting and as a top dressing during the growing season.
- Synthetic Fertilizers: These are chemically manufactured and provide nutrients in a readily available form. They work quickly to promote growth but can lead to nutrient leaching and soil degradation if used excessively. Synthetic fertilizers should be applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions, usually at the start of the growing season and during key growth phases of your crops.
By following these watering and fertilizing practices, you can ensure that your vegetable gardening remains healthy, productive, and full of flavorful harvests.
8. Pest and Disease Management
Maintaining a healthy vegetable garden requires attention to pest and disease management. Identifying common threats and implementing effective control methods can help ensure a fruitful harvest.
Common Pests and Diseases in Vegetable Gardens
Vegetable gardens often face challenges from pests and diseases. Some common pests include aphids, cutworms, and caterpillars, which can damage leaves and stems.
Fungal diseases, like powdery mildew and blight, can affect various plants, leading to wilting, discoloration, and reduced yields.
Regular monitoring of your plants is essential for early detection, allowing you to address issues before they escalate.
Organic Methods for Controlling Pests and Preventing Diseases
There are several organic methods to manage pests and prevent diseases in your garden.

- Beneficial Insects: Encourage the presence of beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, which naturally prey on harmful pests. Planting a variety of flowers can attract these helpful insects to your garden.
2. Neem Oil and Insecticidal Soaps: These organic solutions can help control pest populations without harming beneficial insects. Applying neem oil or insecticidal soap regularly can disrupt the life cycle of pests.


3. Crop Rotation: Rotating crops each year helps disrupt pest and disease cycles. Different crops require different nutrients, which can keep soil healthy and reduce the likelihood of pests accumulating.
Healthy Practices: Practicing good garden hygiene, such as removing dead leaves and debris, can prevent diseases from spreading. Spacing plants correctly improves air circulation, reducing humidity and the risk of fungal infections.

By incorporating these organic methods into your vegetable gardening routine, you can effectively manage pests and diseases while promoting a sustainable and productive vegetable gardening space.
9. Harvesting Techniques
Harvesting vegetables at the right time is crucial for obtaining the best flavor and texture. Understanding signs of readiness and employing best practices will help you maximize yield and maintain plant health for future harvests in your vegetable gardening.
Signs of Readiness for Harvesting Different Vegetables
Different vegetables have unique signs indicating they are ready for harvest:
- Leafy Greens: For vegetables like lettuce and spinach, harvest when the leaves are tender but before they start to bolt (flower). Generally, this is when the leaves are 4-6 inches tall.
- Root Vegetables: Carrots and radishes can be harvested when they reach a desirable size, typically 1-2 inches in diameter for radishes. Pull gently from the soil to avoid damage.
- Fruiting Vegetables: Tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers should be harvested when they have reached their full color and size. Tomatoes should feel slightly soft to the touch, while peppers can be picked when they are firm.
- Beans and Peas: These are best harvested when the pods are plump but before they dry out. Snap the pods off the plant when they are still bright in color.
Best Practices for Harvesting to Ensure Continued Yield
To support ongoing productivity in your vegetable garden, follow these best practices during harvesting:
- Use the Right Tools: Equip yourself with sharp, clean tools such as scissors or garden shears to prevent crushing the plants. This will help avoid damaging the remaining crops.
- Harvest at Optimal Times: Early morning or late afternoon is the best time to harvest, as the vegetables are cooler and hydrated, making them more crisp and flavourful.
- Avoid Overharvesting: Be mindful not to strip too many fruits or leaves from any single plant at once. Leaving some produce on the plant allows it to continue growing and helps maintain its vitality.
- Handle with Care: Gently place harvested vegetables in a basket or container to avoid bruising, and keep them cool and shaded to maintain freshness before storage or processing.
By paying attention to signs of maturity and adhering to these harvesting practices, you can enjoy a bountiful supply of healthy vegetables while supporting the growth of your vegetable gardening space.
10. Season Recap and Future Planning
Reflecting on the gardening season is an important step in improving your skills and ensuring future success. Take some time to evaluate what worked well and what challenges you faced. Consider factors such as plant performance, pest issues, and overall yield. Keeping a garden journal can be useful for tracking these details, helping you make informed decisions in the future.
Based on your experiences this season, here are some tips for planning the next growing season:
- Assess Plant Choices: Review the types of vegetables you grew and their productivity. Consider experimenting with new varieties or sticking to those that thrived to refine your selection for next year.
- Plan for Crop Rotation: Remember to rotate crops to prevent soil depletion and reduce pest and disease buildup. This practice encourages a healthier garden ecosystem.
- Optimize Planting Dates: Use your observations from this growing season to better time your planting. Note the first and last frost dates in your area to avoid planting too early or too late.
- Enhance Soil Health: Reflect on your soil management practices. Plan to improve soil health by adding organic matter or cover crops during the off-season, ensuring a strong foundation for future growth.
- Adjust Watering and Fertilizing Schedules: Based on your notes, adapt your watering and fertilising practices. Consider the weather patterns from this season and how they affected plant health to refine your approach.
By taking the time to reflect and plan, you will build on this year’s successes and address any shortcomings, setting yourself up for a fruitful and enjoyable vegetable gardening experience in the next season.
Conclusion
As we wrap up this guide to successful vegetable gardening, it’s essential to recap the key points that can lead to a thriving garden.
Utilize organic methods such as attracting beneficial insects, applying neem oil, and practicing crop rotation to manage pests and maintain plant health.
Recognizing the signs of readiness for harvesting ensures you enjoy vegetables at their finest, while best practices during the harvest help sustain your garden’s productivity.
As you reflect on this season, take the time to assess what worked well and what could be improved.
Now is the perfect moment to start planning for your next vegetable gardening season. Consider what vegetables to grow, when to plant, and how to enhance your soil health.
With thoughtful preparation and the lessons learned from your vegetable gardening experiences, you can cultivate a productive and enjoyable vegetable gardening space that flourishes year after year. Happy vegetable gardening!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Seasonal Vegetable Gardening: What to Plant and When
- What vegetables can I plant in spring?
- In spring, ideal vegetables to plant include lettuce, spinach, radishes, peas, and carrots. These cool-season crops thrive in the cooler temperatures of early spring.
- When should I plant summer vegetables?
- Summer vegetables, such as tomatoes, peppers, and zucchini, should be planted after the last frost date in your area, usually around late spring to early summer. Check your local frost dates to time your vegetable gardening planting correctly.
- What are some good fall vegetables to grow?
- Fall is a great time for planting vegetables like kale, broccoli, carrots, and squash. These crops can withstand cooler temperatures and can often be harvested late into the season.
- How can I determine my planting zone?
- You can determine your planting zone by referring to USDA Plant Hardiness Zone maps, which consider the average annual minimum temperature in your area, helping you choose suitable plants for your vegetable gardening.
- What should I do if there’s an unexpected frost?
- If a frost threatens your plants, cover them with frost cloths or old bedsheets. If you have potted plants, you can bring them indoors or into a sheltered area to protect them.
- How important is crop rotation and why?
- Crop rotation is essential to maintain soil health, prevent pest and disease buildup, and improve yields. By changing the location of different crops each year, you can help ensure better growth and soil fertility.
- What should I consider when timing my planting?
- Consider local frost dates, the growth time required for each vegetable, and seasonal weather patterns. Timing is key to ensuring that crops can mature before adverse weather conditions arrive in your vegetable gardening.
- Can I grow vegetables year-round?
- Yes, with proper planning and techniques like using cold frames or greenhouses, you can grow certain vegetables year-round. Choosing hardy varieties can extend your growing season significantly.
- What is the best way to prepare my garden for different seasons?
- Preparing for different seasons involves soil testing, adding organic matter, planning crop rotation, and adjusting watering and fertilizing schedules based on seasonal needs in your vegetable gardening.
- How do I find reliable planting calendars?
- You can find reliable planting calendars from local agricultural extensions, gardening books, or educational websites that focus on regional gardening practices. Apps and gardening journals can also help you track planting times.