Kitten Health Care: Vet Visits, Vaccinations, and More
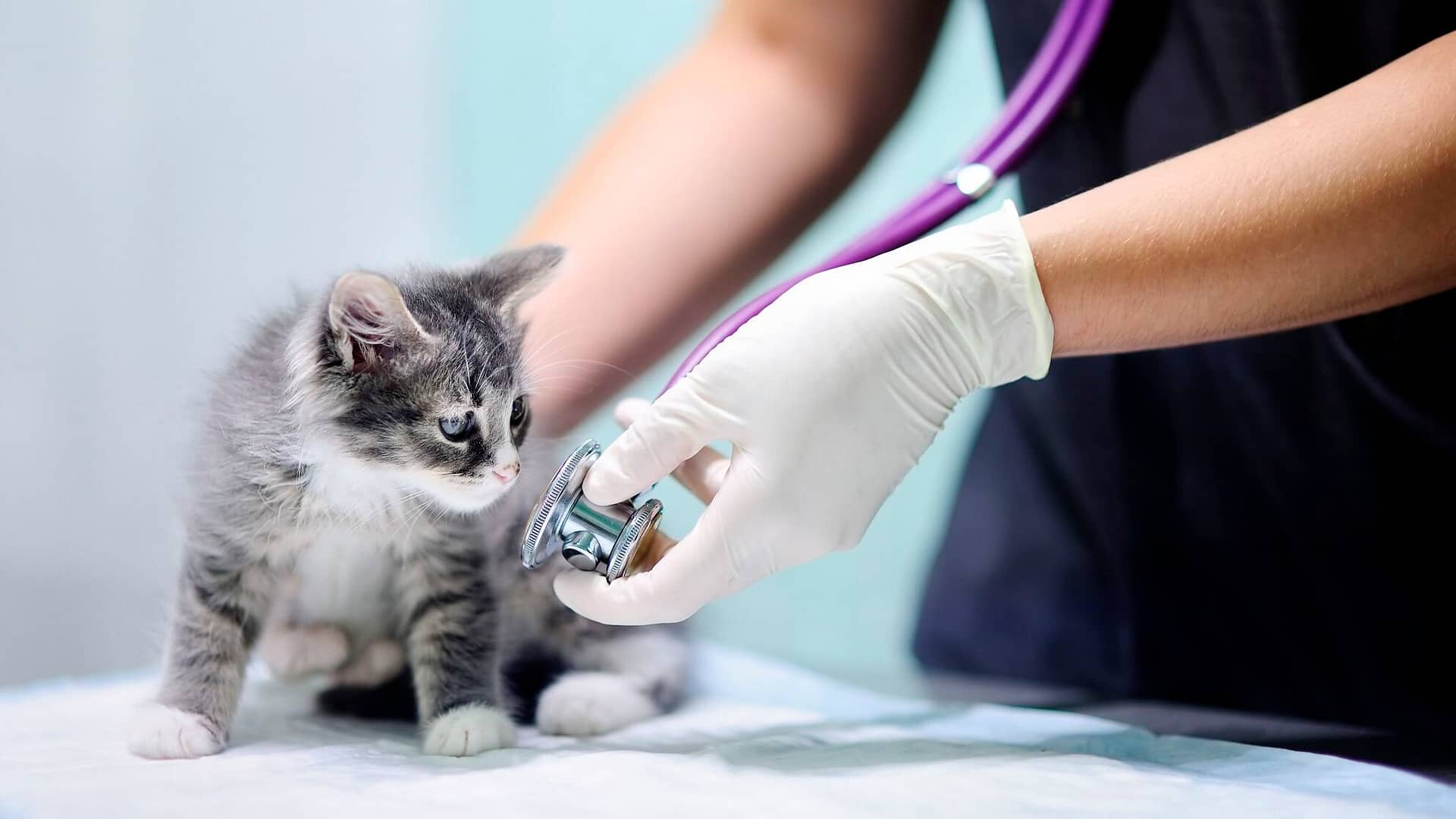
Welcoming a kitten into your home is an exciting and joyful experience, but it also comes with the important responsibility of ensuring their health and well-being. Proper kitten health care is crucial to setting the foundation for a long, happy, and healthy life for your new furry friend.
In this blog post, we will explore key aspects of kitten health care, including essential vet visits, vaccinations, regular health check-ups, dental care, parasite prevention and control, and the benefits of spaying or neutering.
Understanding these fundamentals will help you provide the best care possible for your kitten, ensuring they thrive in their new environment.
Table of Contents
1. The First Vet Visit
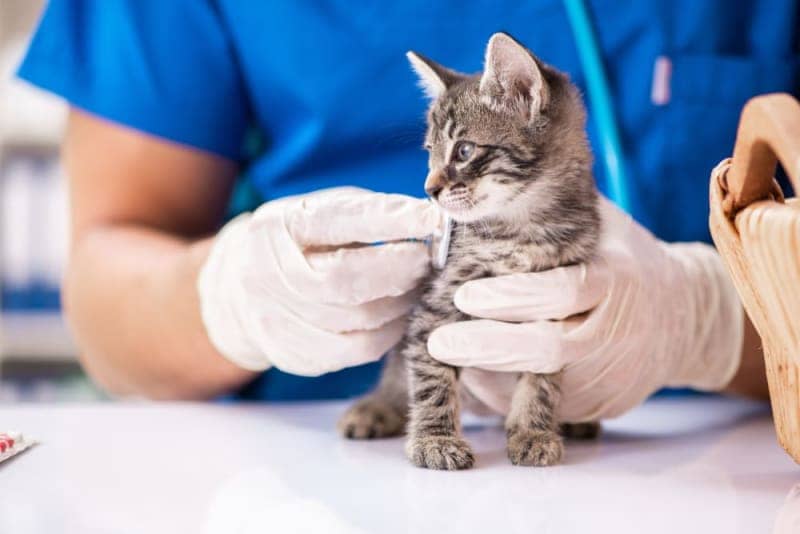
When to Schedule the Initial Vet Appointment
The first vet visit for your kitten should ideally be scheduled within the first week of bringing them home.
Early veterinary care is essential to identify any underlying health issues and to begin necessary vaccinations and treatments.
If possible, arrange for the visit while your kitten is still feeling secure and stress-free in their new environment.
What to Expect During the First Visit
During the initial vet visit, your veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination of your kitten. This includes checking their eyes, ears, mouth, skin, and coat for any signs of illness or abnormalities. The vet will also listen to your kitten’s heart and lungs to ensure they are functioning properly.
Additionally, your kitten may receive their first set of vaccinations, deworming treatment, and flea prevention. This visit is also an opportunity for you to ask any questions you may have about your kitten’s health, diet, and behavior.
Importance of a Comprehensive Health Check
A comprehensive health check during the first vet visit is vital for detecting any potential health concerns early on.
Early detection of issues such as congenital conditions, infections, or parasites allows for prompt treatment, which can significantly improve your kitten’s long-term health prospects.
Moreover, establishing a relationship with your vet from the start provides continuity of care, making future visits more comfortable and effective for both you and your kitten.
2. Vaccinations

Overview of Essential Vaccinations for Kittens
Vaccinations are a critical component of your kitten’s healthcare regimen, helping to protect them from several infectious diseases.
The core vaccinations recommended for all kittens typically include the following:
- Feline Rhinotracheitis Virus (FVR), Calicivirus, and Panleukopenia Virus (FVRCP) Vaccine: Often administered as a combined vaccine, this protects against upper respiratory infections and feline distemper.
- Rabies Vaccine: Mandatory in many areas, the rabies vaccine is crucial for preventing this fatal disease.
- Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) Vaccine: While not always considered a core vaccine, it is highly recommended for kittens at risk of exposure to the virus.
Timeline for When These Vaccinations Should Be Administered
Kittens should receive their initial vaccinations starting at around 6 to 8 weeks of age. The vaccination schedule generally follows this timeline:
- 6-8 weeks: First dose of FVRCP vaccine.
- 10-12 weeks: Second dose of FVRCP vaccine and first dose of FeLV vaccine if at risk.
- 14-16 weeks: Third dose of FVRCP vaccine, second dose of FeLV vaccine, and the rabies vaccine.
Your vet may adjust this schedule based on your kitten’s specific needs and health status. Booster shots will also be necessary to maintain immunity as your kitten grows into an adult cat.
Benefits of Vaccinating Your Kitten
Vaccinating your kitten provides substantial benefits, including:
- Disease Prevention: Vaccinations protect against severe and potentially life-threatening diseases, reducing the risk of illness and death.
- Community Health: Widespread vaccination helps prevent the spread of contagious diseases, contributing to the overall health of the feline population.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your kitten is protected allows you to enjoy their companionship without the constant worry of them contracting preventable diseases.
- Cost Savings: Preventing disease through vaccination can save you significant costs in veterinary treatments and hospitalization should your kitten fall ill.
By adhering to the recommended vaccination schedule, you are taking a proactive step to ensure the long-term health and happiness of your kitten.
3. Regular Health Check-Ups

Recommended Frequency for Vet Check-Ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are integral to ensuring your kitten’s ongoing health and well-being. During the first year of life, it is recommended to schedule vet visits every 3 to 4 weeks.
These frequent check-ups allow the vet to monitor your kitten’s growth and development, administer necessary booster vaccinations, and address any health concerns early.
After the first year, transitioning to annual or semi-annual check-ups helps maintain their health through adulthood.
Common Health Issues to Monitor as Kittens Grow
As kittens grow, they may encounter a variety of health issues. Common concerns include:
- Respiratory Infections: Kittens are prone to upper respiratory infections, which can manifest as sneezing, nasal discharge, and coughing.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Diarrhea, constipation, and vomiting can occur due to dietary changes, parasites, or infections.
- Parasites: Monitoring for fleas, ticks, and internal parasites like worms is crucial, as they can severely impact your kitten’s health.
- Dental Problems: Early signs of dental disease, such as inflamed gums and bad breath, should be addressed to prevent more serious conditions.
- Congenital Conditions: Some kittens may be born with congenital conditions that can affect their heart, kidneys, or other vital organs.
Preventative Care Tips to Maintain Overall Health
Preventative care goes a long way in ensuring your kitten remains healthy and happy. Key tips include:
- Balanced Diet: Provide a nutritious, balanced diet suitable for kittens to support optimal growth and development.
- Regular Exercise: Engage your kitten in play and activities to promote physical and mental stimulation.
- Dental Hygiene: Start brushing your kitten’s teeth early and provide dental treats to maintain oral health.
- Parasite Control: Use recommended flea, tick, and deworming treatments as advised by your vet.
- Hydration: Ensure fresh, clean water is always available to keep your kitten well-hydrated.
- Safe Environment: Create a safe and enriched environment for your kitten, free from hazards and full of engaging toys and structures.
By adhering to these preventative care measures and maintaining regular vet check-ups, you will help your kitten grow into a healthy and thriving adult cat.
4. Dental Care

Importance of Dental Hygiene in Kittens
Maintaining good dental hygiene in kittens is essential for their overall health and well-being.
Dental issues can lead to pain, and infection, and even affect your kitten’s ability to eat and grow. Bad oral health can also have systemic impacts, potentially leading to more severe conditions like heart disease.
By establishing healthy dental habits early on, you can prevent many common dental problems and ensure that your kitten’s teeth and gums remain healthy as they mature.
Steps to Care for Your Kitten’s Teeth
Proper dental care for your kitten involves several key steps:
- Introduce Brushing Early: Start brushing your kitten’s teeth as early as possible to get them accustomed to the process. Use a toothbrush and toothpaste specifically designed for cats.
- Regular Brushing: Aim to brush your kitten’s teeth at least a few times per week. Consistency is crucial in preventing the build-up of plaque and tartar.
- Dental Treats and Toys: Provide dental treats and toys designed to promote oral health. These can help clean teeth and massage gums.
- Professional Cleanings: Schedule professional dental cleanings with your vet as needed. These cleanings are more thorough and can address issues that regular brushing might miss.
- Balanced Diet: Offer a diet that supports dental health. Some cat foods are specifically formulated to reduce plaque and tartar build-up.
Signs of Dental Problems
It is important to monitor your kitten for any signs of dental issues. Common indicators include:
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath could signify dental disease or infection.
- Red, Inflamed Gums: Gingivitis is an early stage of periodontal disease and can cause redness and swelling of the gums.
- Difficulty Eating: If your kitten is reluctant to eat or seems to be in pain while chewing, it might have dental problems.
- Excessive Drooling: Drooling can be a sign of oral discomfort or dental disease.
- Brown or Yellow Teeth: Discoloration on the teeth may indicate the presence of plaque and tartar.
- Pawing at the Mouth: If your kitten frequently paws at its mouth, it could be experiencing dental discomfort.
By paying attention to these signs and incorporating regular dental care practices, you can help prevent serious dental diseases and keep your kitten’s mouth healthy and pain-free.
5. Parasite Prevention and Control

Common Parasites That Affect Kittens
Kittens are particularly vulnerable to a variety of parasites, which can significantly impact their health. The most common parasites include:
- Fleas: These small, wingless insects can cause intense itching, and anemia, and transmit other parasites like tapeworms.
- Ticks: Ticks attach themselves to your kitten’s skin, feeding on their blood and potentially transmitting serious diseases such as Lyme disease.
- Worms: Intestinal worms, including roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms, can lead to malnutrition, diarrhea, and weight loss. Heartworms, which affect the heart and lungs, can be life-threatening.
Preventative Treatments and Best Practices
Preventing parasite infestations is crucial for maintaining your kitten’s health. Effective practices and treatments include:
- Regular Vet Visits: Regular check-ups allow your vet to identify and treat any parasitic infections early.
- Flea and Tick Preventatives: Use vet-recommended topical treatments, oral medications, or collars designed to repel and kill fleas and ticks.
- Deworming: Deworm your kitten according to your vet’s schedule, typically starting from a young age and continuing at regular intervals.
- Environmental Control: Keep your home and yard clean to reduce the risk of exposure to parasites. Regularly wash bedding and vacuum thoroughly.
- Avoid Contact with Other Animals: Until your kitten is fully vaccinated and dewormed, limit their exposure to other animals that may carry parasites.
Signs and Symptoms of Parasitic Infections
Early detection of parasitic infections can prevent complications. Watch for the following signs and symptoms:
- Scratching and Biting: Excessive scratching or biting at the skin can indicate a flea or tick infestation.
- Visible Parasites: Fleas, ticks, or worms may be visible on your kitten or in their stool.
- Coughing or Difficulty Breathing: These can be symptoms of a heartworm infection.
- Vomiting and Diarrhea: Both can be signs of intestinal worms or protozoan infections.
- Weight Loss: Despite a normal or increased appetite, weight loss can occur if worms are present.
- Lethargy and Anemia: A heavy infestation of parasites can cause your kitten to become lethargic and anemic, due to blood loss and nutrient depletion.
By implementing effective preventative measures and staying vigilant for signs of infection, you can protect your kitten from the harmful effects of parasites and ensure they grow into healthy adult cats.
6. Spaying and Neutering
Benefits of Spaying/Neutering Your Kitten
Spaying and neutering your kitten offer numerous benefits for their health and well-being.
These procedures can prevent various health issues, including uterine infections and breast tumors in females and testicular cancer and prostate problems in males. Additionally, spaying and neutering can reduce undesirable behaviors such as yowling, marking territory, and aggression, making your kitten easier to live with.
It also helps to prevent overpopulation and reduces the number of unwanted kittens.
When to Consider Having This Procedure Done
The ideal time to have your kitten spayed or neutered typically ranges between 4 and 6 months of age, although it can be done earlier or later depending on your vet’s advice and your kitten’s individual health and development.
Early spaying/neutering can have additional benefits, such as a quicker recovery time and better long-term health outcomes.
Discuss with your veterinarian to determine the best timing for your kitten based on their specific needs.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery Tips
Post-surgery care is essential to ensure a smooth recovery for your kitten:
- Rest and Restricted Activity: Keep your kitten calm and limit their physical activity for at least ten days after the surgery to prevent complications such as tearing the surgical incision.
- Monitor the Incision Site: Check the incision site daily for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. Contact your vet if you notice anything unusual.
- Prevent Licking and Chewing: Use an e-collar (cone) to prevent your kitten from licking or chewing at the incision site, which can cause infections or open the wound.
- Follow Dietary Recommendations: Feed your kitten small, easily digestible meals for the first 24 hours following surgery. Gradually return to their regular diet as advised by your vet.
- Administer Medications: Give your kitten any prescribed medications, such as pain relievers and antibiotics, exactly as directed by your veterinarian.
- Limit Interactions with Other Pets: Keep your recovering kitten separated from other pets to prevent rough play and reduce stress.
By understanding the benefits, appropriate timing, and proper post-surgery care, you can help ensure your kitten’s spaying or neutering procedure is successful and their recovery is swift and uneventful.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining your kitten’s health involves understanding and addressing common parasites, ensuring timely spaying or neutering, and providing diligent post-surgery care.
We discussed the importance of regular vet visits, which help in early detection and treatment of parasitic infections. Employing flea and tick preventatives, adhering to a deworming schedule, and practicing environmental control are crucial steps in safeguarding your kitten against parasites.
Additionally, spaying and neutering offer significant health benefits and can minimize undesirable behaviors, contributing to a better quality of life for your pet.
Regular veterinary check-ups and a consistent health care routine are paramount in ensuring your kitten grows into a robust and lively adult cat.
By staying proactive and informed, you can protect your kitten from potential health issues, allowing them to thrive. Proper health care not only enhances your kitten’s well-being but also strengthens the bond you share.
Remember, a healthy kitten is a happy kitten, and your efforts in maintaining their health will lead to a lifetime of companionship and joy.





